×
Stainless steel stands out for its corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and various surface finishes (raw, brushed, polished, or mirror), making it a benchmark material for permanent marking.
These properties directly influence the choice of marking technology: grade hardness, surface reflectivity level, contrast requirements, depth requirements, or preservation of the passive layer. Depending on the application, marking can be performed without material removal using laser annealing, or with controlled depth through laser engraving or mechanical processes, according to environmental and usage constraints.
When properly controlled and validated, these parameters make it possible to achieve a precise, durable, and readable mark, suitable for both visual inspection and camera-based reading—an essential condition for traceability, identification, and regulatory compliance in demanding industrial environments.
Depending on the stainless steel grade (304, 316, 420, duplex stainless steel), its hardness, reflectivity level, or surface finish (raw, brushed, polished, mirror), SIC MARKING offers three permanent marking technologies adapted to stainless steel marking, selecting the most relevant solution based on material properties, application constraints, and marking durability requirements.
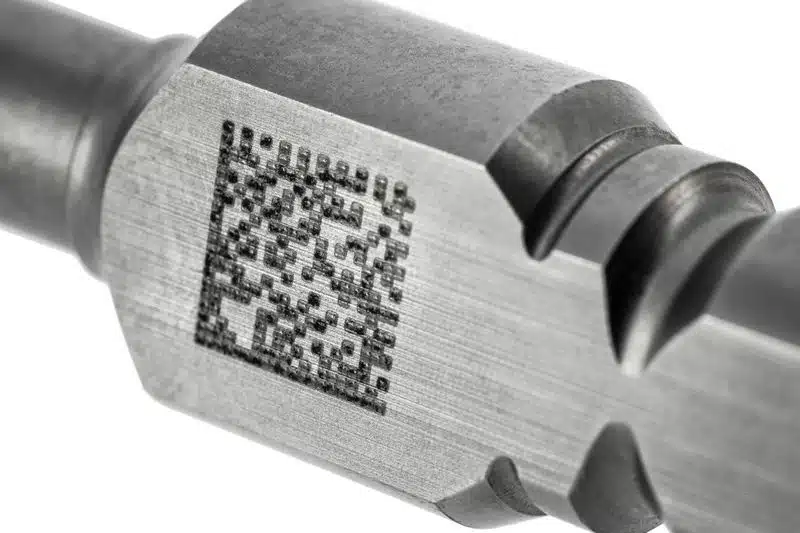
Depending on the type of stainless steel, its hardness, surface finish, and the final use of the part, the choice of permanent marking technology for stainless steel must be carefully adapted to ensure readability, durability, and functional integrity.
In industry, there are mainly five stainless steel families: austenitic (stainless steel 304, stainless steel 316), ferritic (stainless steel 430, stainless steel 444), duplex (stainless steel 2205), martensitic (stainless steel 410, stainless steel 420), and precipitation-hardening (17-4PH).
They differ in composition, magnetic properties, and mechanical strength, parameters that directly influence their response to laser and mechanical marking processes.
In a stainless steel marking solution, these differences between stainless steel families guide the choice of technology (laser, dot peen, or scribing) and process settings, in order to achieve durable marking without altering the functional properties of the part.
Laser marking on stainless steel, using annealing or micro-ablation, provides high contrast and excellent precision. Laser annealing, with no material removal, is preferred when corrosion resistance and preservation of the passive layer are critical, while micro-ablation is used when readability and mechanical durability of the marking are the priority.
Stainless steel marking by dot peen and scribing, both mechanical processes, remains particularly well suited to thick parts, harsh environments, and certain surface conditions, when marking depth and robustness are the main requirements.
Stainless steel hardness
Geometry of the stainless steel part
Marking objective
Stainless steel part thickness and rigidity
Complex shapes
Marking finesse
Appearance durability
Environmental constraints
Stainless steel is particularly well suited for permanent marking, provided that the technology and parameters are properly selected.
Its stable surface responds especially well to laser marking, enabling high contrast and excellent long-term marking durability.
Depending on its grade and surface condition, stainless steel responds favorably to laser marking, achieving high contrast and durable markings over time.
According to the application, it allows for DPM DataMatrix codes, QR codes, barcodes, serial numbers, or logos, using laser marking, dot peen marking, or scribing, with depth and contrast levels tailored to usage requirements and the part’s environment.
The selection of stainless steel marking technology is based on three measurable and complementary criteria: machine readability (industrial vision), marking durability — resistance to abrasion and solvents — and aesthetic resolution, particularly for visible parts or those requiring high-quality finishes.
Laser marking and dot peen marking are among the most commonly used processes for stainless steel marking, each serving distinct functional objectives. Laser marking stands out for its high contrast and ability to integrate into high-speed production lines, while dot peen marking ensures high mechanical durability, particularly suited for outdoor environments and harsh industrial conditions.

In workshops, the DataMatrix ECC200 is widely recognized as a standard for industrial traceability. It can encode up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters, although direct marking applications typically use significantly smaller amounts of information.
When properly executed, the DataMatrix ECC200 remains reliably readable by industrial cameras, even on challenging surfaces such as brushed stainless steel or polished stainless steel, provided camera reading validation is performed.
In industrial practice, typical DPM DataMatrix code sizes generally range between 4 and 12 mm, depending on information density, achieved contrast, and vision system resolution.
When produced with a laser using appropriate contrast and geometry, DataMatrix codes achieve high reliability for camera reading in industrial environments.

QR codes are generally preferred for user-oriented marking: they provide direct access, via smartphone or tablet, to technical datasheets, URLs, installation videos, or regulatory information associated with the product.
Their high encoding capacity—reaching several thousand characters depending on the code version—allows the integration of complex data. In industrial production, a minimum size typically ranging between 8 and 15 mm is usually adopted to ensure stable readability, particularly on challenging surfaces such as brushed stainless steel, provided camera reading validation is performed.
In industrial environments, laser marking of stainless steel ensures the sharpness of modules required for QR codes of low to medium density, with excellent repeatability and good compatibility with reading devices.
Dot peen marking remains feasible for this type of marking but produces wider, less uniform modules, requiring larger overall code dimensions to maintain readability, especially on small surfaces.

Serial numbers on stainless steel ensure both product identification and industrial traceability throughout the part’s lifecycle. They can be purely numeric, alphanumeric, or follow standardized formats, such as the automotive VIN (17 characters) or UDI identifiers for medical devices, depending on regulatory and industry requirements.
Laser marking of serial numbers provides high contrast on brushed stainless steel, polished stainless steel, or raw stainless steel, and can be integrated into high-speed production lines, depending on automation level and equipment configuration.
Dot peen marking offers high mechanical durability in abrasive or high-stress environments, while scribing delivers a premium aesthetic finish, particularly valued for nameplates or decorative stainless steel applications.

Stainless steel enables the reproduction of logos and pictograms with high precision: very small details can be achieved via laser marking on brushed, satin, or polished stainless steel surfaces, maintaining readability and contrast, provided the process and parameters are adapted to chemical treatments or industrial washing.
Regulatory symbols (CE marking, crossed WEEE bin, PPE pictograms) as well as directional arrows are particularly suited for laser marking on stainless steel, offering clean, precise outlines without part deformation and meeting readability standards.
Dot peen marking remains a relevant solution in highly abrasive environments, when marking depth takes priority over aesthetic appearance.
Brand logo marking on stainless steel serves a dual purpose: functional identification and aesthetic enhancement. A fine laser marking, performed via annealing or controlled micro-ablation, delivers a “premium” finish on visible parts, while recessed dot peen marking enhances durability for components subjected to friction or repeated mechanical stress.
Industrials in the electronics and automotive sectors commonly use laser marking on stainless steel to reproduce complex logos and serial numbers on technical components, ensuring high uniformity and excellent repeatability across batches of several thousand units.
Stainless steel, thanks to its natural corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and surface finish quality (brushed, polished, or raw), is particularly well suited for permanent marking using laser, dot peen, or scribing.
These stainless steel marking technologies allow, depending on the chosen process, precise, high-contrast, or deep markings, ensuring long-lasting readability, provided the technology and parameters are adapted to exposure conditions such as humidity, intensive cleaning, or abrasion.
Permanent marking on stainless steel parts thus meets the traceability and regulatory compliance requirements of industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, food processing, and railway.





Contact Us
Need information?
Get in touch with one of our experts!